As more and more households rely on TVs for entertainment and information, it’s essential to know how much energy your television consumes. The power consumption of a TV can significantly impact your electricity bill and the environment. In this article, we’ll provide you with a detailed guide on the topic how many watts does a TV Use, how it varies based on different factors, and some tips to reduce your energy consumption.

Understanding Watts and Power Consumption
Before we dive into the power consumption of TVs, it’s essential to understand the unit used to measure electrical power – Watts. One watt is equivalent to one joule per second, representing the rate at which energy is consumed or produced. In other words, it’s a measure of how much energy is used in a particular period.
The power consumption of electrical devices is usually measured in watts per hour or kilowatts per hour (kWh). One kilowatt is equivalent to 1000 watts, and it’s commonly used to measure the energy consumption of households.
How Many Watts Does a TV Use?
The power consumption of a TV varies based on several factors, such as the type of TV, size, display technology, and usage. Let’s explore each factor in more detail.
Average Power Consumption of Different TV Types
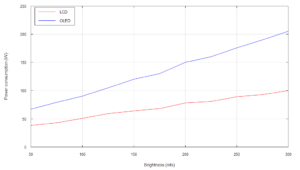
There are mainly four types of TVs in the market – LCD, LED, OLED, and Plasma. Each type of TV has different power consumption levels due to their unique technology.
- LCD TVs: On average, an LCD TV consumes 50-100 watts per hour, depending on the size and brightness level.
- LED TVs: LED TVs use slightly less power than LCD TVs, consuming around 30-100 watts per hour.
- OLED TVs: OLED TVs are more energy-efficient than LCD and LED TVs, consuming around 50-90 watts per hour.
- Plasma TVs: Plasma TVs are the least energy-efficient and consume around 150-300 watts per hour.
Power Consumption of TVs Based on Size
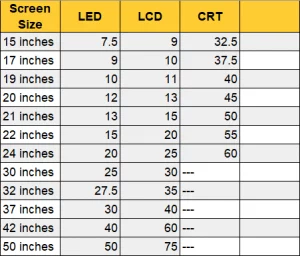
The size of the TV is another significant factor that affects power consumption. Generally, larger TVs consume more energy than smaller ones.
- 32-inch TV: An average 32-inch TV consumes 30-70 watts per hour.
- 42-inch TV: A 42-inch TV consumes around 55-110 watts per hour.
- 55-inch TV: A 55-inch TV consumes around 60-130 watts per hour.
- 65-inch TV: A 65-inch TV consumes around 110-180 watts per hour.
Power Consumption of TVs Based on Display Technology
The display technology also plays a vital role in determining the power consumption of a TV.
- LCD and LED TVs: The power consumption of LCD and LED TVs varies depending on their size and features. The backlight of an LCD TV is the biggest power consumer, while the LED backlight of an LED TV consumes less power. This TV has a best tv size for bedroom. The power consumption of an LCD or LED TV can range from 20 watts for a small 32-inch model to over 100 watts for a large 55-inch model.
- OLED TVs: OLED TVs are known for their energy efficiency because they don’t require backlighting. Instead, each pixel on an OLED TV emits its own light, allowing for more precise and efficient power consumption. The power consumption of an OLED TV is significantly lower compared to an LCD or LED TV of the same size. For instance, a 55-inch OLED TV consumes approximately 100-150 watts, which is significantly lower than a 55-inch LED TV that can consume up to 250 watts.
- Plasma TVs: Plasma TVs are known for their high power consumption compared to other display technologies. They use gas-filled cells to produce images, and they require high levels of energy to function. As a result, the power consumption of a plasma TV can range from 200 watts for a small 42-inch model to over 400 watts for a large 60-inch model.
Tips for Reducing TV Power Consumption
1. Adjust Brightness and Contrast
Reducing the brightness and contrast of your TV can significantly reduce its power consumption. Brighter screens require more power, so lowering these settings can save energy.
2. Enable Power Saving Mode
Most modern TVs have a power-saving mode that reduces power consumption by automatically adjusting the brightness, contrast, and other settings based on the ambient light in the room. Enabling this feature can help save energy.
3. Turn Off When Not in Use
Turning off your TV when not in use is the easiest and most effective way to save power. Avoid leaving your TV on standby mode as it still consumes power. It is easier to turn off multiple devices at once with a power strip.
4. Use Eco-Friendly Features
Some TVs come with eco-friendly features such as motion sensors that detect when there is no one in the room and automatically turn off the TV. These features can help reduce power consumption.
5. Use a Smaller TV
As the TV gets larger, it consumes more power. Consider using a smaller TV if it suits your needs. A 32-inch TV consumes significantly less power than a 55-inch TV.
6. Avoid 4K and HDR
4K and HDR (High Dynamic Range) are display technologies that significantly increase power consumption. If you are concerned about power consumption, consider purchasing a TV without these features.
7. Purchase an Energy-Efficient TV

Look for TVs with an Energy Star rating or other energy-efficient certifications. These TVs are designed to consume less power while still providing high-quality images and features.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the power consumption of a TV varies depending on various factors such as the display technology, screen size, and additional features. LCD and LED TVs consume more power compared to OLED TVs, while plasma TVs are known for their high power consumption. It’s important to consider energy efficiency ratings and features such as power-saving modes when purchasing a TV to reduce power consumption.
To reduce TV power consumption, you can adjust brightness and contrast, enable power-saving mode, turn off the TV when not in use, use eco-friendly features, consider a smaller TV, avoid 4K and HDR, and purchase an energy-efficient TV. By implementing these tips, you can reduce the energy consumption of your TV and save money on your electricity bill while still enjoying your favorite shows and movies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q.1 How many watts does a TV use per hour?
The wattage of a TV can vary depending on the display technology, screen size, and other factors. However, on average, a TV can use between 80 to 400 watts per hour.
Q.2 How many watts does a 24-inch TV use?
The wattage of a 24-inch TV can range from 20 to 50 watts depending on the display technology. An LCD or LED TV may use 20 to 30 watts, while an OLED TV may use up to 50 watts.
Q.3 Is it Possible a tv as a computer monitor?
Most of the peoples query “can i use a tv as a computer monitor“, So the answer is Yes, it is possible to use a TV as a computer. However, there are some things to consider, such as the difference in display quality, audio options, and connectivity. TVs are designed for watching videos from a distance and have a lower pixel density compared to computer monitors. As a result, text and icons may appear blurry on a TV. Additionally, TV speakers are often not as powerful as computer speakers. Despite these drawbacks, using a TV as a monitor can be a cost-effective way to create a larger display.
Q.4 How many watts does a flat screen TV use?
The wattage of a flat-screen TV can vary depending on the display technology, screen size, and other factors. On average, a 55-inch flat-screen TV may use around 80 to 400 watts, while a 32-inch flat-screen TV may use around 20 to 50 watts. It’s important to check the manufacturer’s specifications for the exact wattage of your TV.